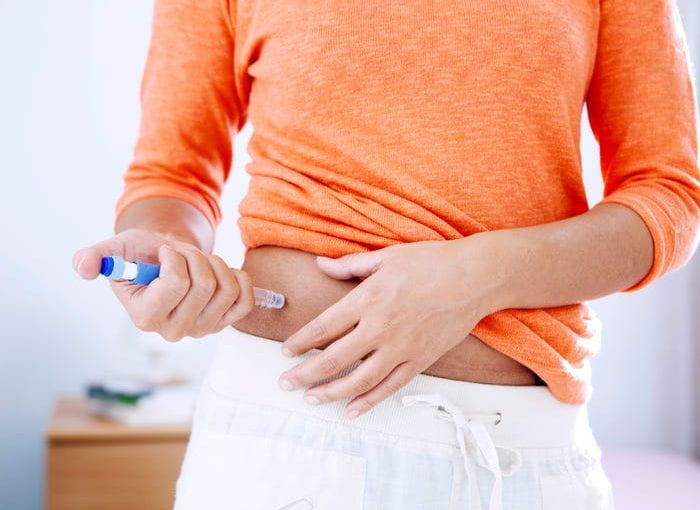
Mounjaro injections have gained significant attention for their role in metabolic regulation. Designed to enhance the body’s natural ability to process energy, these injections work by targeting key metabolic pathways. Doctors utilize Mounjaro as part of a comprehensive treatment strategy to support patients in improving metabolic efficiency and overall health. For those seeking advanced metabolic care, Mounjaro Injections in Dubai are becoming an increasingly popular option, offering innovative solutions for better health management.
Understanding Metabolism and Its Role
Metabolism is the process by which the body converts food into energy. A well-functioning metabolism ensures efficient calorie burning, stable blood sugar levels, and overall energy balance. However, factors such as genetics, age, and lifestyle can lead to a slower metabolism, making it harder to maintain optimal health.
How Doctors Approach Metabolism Enhancement
Medical professionals use a patient-centered approach when incorporating Mounjaro into treatment plans. Before prescribing the injections, doctors conduct thorough evaluations, considering factors such as medical history, lifestyle, and metabolic rate.
Mechanism of Action in Metabolism Regulation
Mounjaro injections influence specific metabolic pathways, helping the body regulate energy production and glucose utilization. Doctors explain that these injections work by activating hormonal responses that improve insulin sensitivity, curb appetite, and promote energy balance. By enhancing these functions, Mounjaro supports a more efficient metabolic system.
Personalized Treatment Plans by Specialists
Each patient has unique metabolic needs, and healthcare providers tailor treatment plans accordingly. Physicians monitor progress regularly, adjusting the approach based on the patient’s response to the injections. This personalized strategy ensures that Mounjaro is used effectively to optimize metabolism.
Long-Term Monitoring and Lifestyle Integration
Doctors emphasize that while Mounjaro injections play a role in metabolic improvement, they work best when combined with a healthy lifestyle. Regular follow-ups help track progress, and medical experts provide guidance on nutrition, physical activity, and sustainable habits to support long-term metabolic health.
Benefits of Mounjaro for Metabolism
Mounjaro injections offer multiple benefits when prescribed by medical professionals for metabolic regulation. These include:
- Improved Energy Utilization – The body processes nutrients more efficiently, reducing fatigue.
- Better Blood Sugar Control – Enhanced insulin sensitivity supports glucose balance.
- Reduced Cravings – Appetite regulation contributes to a more controlled eating pattern.
- Enhanced Fat Metabolism – Supports the body’s ability to break down stored fat effectively.
- Sustainable Metabolic Support – Long-term improvements when combined with doctor-guided strategies.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Mounjaro directly speed up metabolism?
Yes, it enhances metabolic functions by improving insulin sensitivity and energy regulation.
Can Mounjaro injections help with weight loss?
Yes, they support weight management by reducing appetite and improving fat metabolism.
How long does it take to see metabolic changes?
Results vary, but noticeable improvements often occur within weeks of consistent treatment.
Is Mounjaro safe for long-term metabolic support?
Doctors monitor patients closely to ensure safe and effective long-term use.
Can lifestyle changes enhance Mounjaro’s effectiveness?
Yes, combining injections with healthy habits maximizes metabolic benefits.
Conclusion
Mounjaro injections play a vital role in improving metabolism when used under medical supervision. With personalized treatment plans and ongoing monitoring, doctors help patients achieve sustainable metabolic health.